반응형

[문과 코린이의 IT 기록장] C# - 배열 및 제어문(배열, 조건문 (IF / SWITCH), 반복문 (For / While / Do While))
C# 프로그래밍 기초 - 인프런 | 강의
본 강좌는 C# 문법 위주로 구성되어있지 않습니다. 클래스를 이해하고 만드는 요령 위주로 구성되어 있습니다. 기초 문법도 다루지만 많은 예제를 가지고 진행하기 때문에 프로그램 실전 작성
www.inflearn.com
1. 배열
배열 : 단 하나의 변수에 여러개의 값을 저장하는 것
a. 1차원 배열 : 변수 이름은 1개 / 변수 앞에 붙는 타입 1개 / [ ] 내의 숫자(인덱스)로 구분해 씀
b. 2차원 배열 : 1차원 배열이 여러개 있는 것
using System; namespace _0801 { public enum Grade { 학년_1 = 1, 학년_2 = 2, 학년_3 = 3 } class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { // 1. int[] kor = new int[10]; // kor이라는 변수는, 10개의 엘리먼트를 갖는 배열로 만들어진다. // 각 엘리먼트에는 index로 접근 가능하다. (인덱스는 0번부터 시작) kor[0] = 10; kor[1] = 20; Console.WriteLine("kor[0] = " + kor[0]); // 2. int[] kor1 = new int[] { 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60 }; // 6개의 엘리먼트를 가지는, 배열 선언 및 초기화 Console.WriteLine("kor1[0] = " + kor1[0]); // 3. string[] name = new string[] { "lee", "kim", "park" }; Console.WriteLine(name[0] + "의 국어 성적 : " + kor[0]); // 4. int[,] kor2 = new int[10, 10]; int[,] kor2_1 = new int[,] { { 10, 20, 30 }, { 30, 90, 100 }, { 40, 50, 120 } }; // 2차원 배열 초기화 : 1반 학생 3명 / 2반 학생 3명 / 3반 학생 3명 // 5. int[,,] kor3 = new int[,,] { { // ex. 1학년 { // ex. 1반 10, // ex. 1번 점수 20, // ex. 2번 점수 30 // ex. 3번 점수 }, { 10, 20, 30 }, // ex. 2반 { 10, 20, 30 } // ex. 3반 }, { { 10, 20, 30 }, { 10, 20, 30 }, { 10, 20, 30 } }, // ex. 2학년 { { 10, 20, 30 }, { 10, 20, 30 }, { 10, 20, 30 } } // ex. 3학년 }; // 3차원 배열 초기화 // 6. OOP의 장점을 살린, 배열 생성 (2차원, 3차원 등을 만들 필요가 없음. 클래스로 구현하면 됨) Student[] st = new Student[10]; // 학생 10명 만들기 (변수 1개로 10명을 처리) st[0] = new Student("kim"); // 1반 st[1] = new Student("lee"); // 2반 st[2] = new Student("cho"); // 3반 // 학년도 고려해 코딩 Student[] st1 = new Student[30]; // 1학년 (각 30명씩) Student[] st2 = new Student[30]; // 2학년 Student[] st3 = new Student[30]; // 3학년 } } // 하나의 클래스 내에는 클래스 X. (main 내부에 작성하면 안됨) class Student { private Grade grade; private int kor; private string name; public Student(string name) { this.name = name; } } }
2. 조건문 (IF / SWITCH)
1) IF문
using System; namespace _0801_if { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { int a = 0; Console.WriteLine("숫자를 입력하세요"); string val = Console.ReadLine(); a = int.Parse(val); Console.WriteLine("a 값은 " + a + "입니다."); if (a == 3) { Console.WriteLine("3입니다"); } else if(a==2) { Console.WriteLine("2입니다."); } else { Console.WriteLine("a 값은 둘 다 아닙니다."); } } } }

2) Switch문
using System; namespace _0801_if { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { Console.WriteLine("숫자를 입력하세요"); string val = Console.ReadLine(); int c = int.Parse(val); switch(c){ case 0: PrintSheet(c); break; case 1: PrintSheet(c); break; case 2: PrintSheet(c); break; default: Console.WriteLine("해당사항 없습니다."); break; } } private static void PrintSheet(int a) { Console.WriteLine(a+"이 입력되었습니다."); } } }

3. 반복문 (For / While / Do While)
1) for문
using System; namespace _0801_if { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { // for () for (int i=0; i<10; i++) { Console.WriteLine("i = " + i); } } } }

2) While문
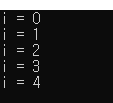
using System; namespace _0801_if { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { // while int i = 0; while (i<5) { Console.WriteLine("i = " + i); i++; } } } }

- 컴퓨터에 있는 파일을 읽어들일 때 주로 사용 ex. readline이 not null일 때까지 수행한다.
- While문은 최소 0바퀴를 돈다. 즉, 한 바퀴도 돌지 않고 빠져나갈 수 있다.
3) Do While
- Do While문은 최소 1바퀴를 돈다. 즉, 한 바퀴도 돌지 않고 빠져나갈 수 없도록 한다.
using System; namespace _0801_if { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { // while int i = 0; do { Console.WriteLine("i = " + i); i++; } while (i < 5); } } }
| * 유의사항 - 아직 공부하고 있는 문과생 코린이가, 정리해서 남겨놓은 정리 및 필기노트입니다. - 정확하지 않거나, 틀린 점이 있을 수 있으니, 유의해서 봐주시면 감사하겠습니다. - 혹시 잘못된 점을 발견하셨다면, 댓글로 친절하게 남겨주시면 감사하겠습니다 :) |
반응형



